Email client protocols and port numbers
Overview
This article is a companion to the Email client configuration overview article. Make sure you first review the ‘Email client configuration’ article for a general overview on how to set up your email in your chosen email client:
Most often, your email client will automatically set secure port values for you. However, if your client makes you enter these port values manually, view the information below to determine the correct values.
The port numbers you set determine the protocol (IMAP or POP) your email client uses. There are four basic options. IMAP secure is the recommended configuration:
- IMAP (secure) — RECOMMENDED
- IMAP (insecure)
- POP3 (secure)
- POP3 (insecure)

Follow the steps below to choose which protocol and port numbers you’d like to use to connect to your mail server.
To quickly find your email settings in the panel, open the Manage Email page and look for the ![]() link in the upper right. Click the text to open the quick-access instructions for your email address:
link in the upper right. Click the text to open the quick-access instructions for your email address:
Incoming
imap.dreamhost.com
pop.dreamhost.com
Outgoing
smtp.dreamhost.com
Step 1 — Decide between POP3 or IMAP
POP3 and IMAP are two different ways of checking mail. A mail client program connects to the mail server using either POP3 or IMAP. All DreamHost mail accounts support both POP3 and IMAP connections automatically.
What is POP3?
POP3 downloads all mail from the server from the Inbox and stores it on your computer. This way, emails are available when you’re not connected to the Internet.
You also have the option (in your mail client) to keep email on the server. If you choose not to enable this setting in your mail client, the emails are removed from the server and only stored locally in your mail client program.
The POP setup will only download mail from the Inbox folder. Any other emails in folders or sub-folders (such as Trash, Draft, and Sent) must be moved to the Inbox in order for that to be viewed or downloaded via POP.
What is IMAP?
IMAP syncs your mail client program with the server. Emails stay on the server, and you can make and view mail folders on the server in addition to the Inbox. Most mail client program have a feature to initially sync just the email headers, so you can quickly see what emails you have, then download the message body when you want to read the email. Since emails stay on the server, you can see all your emails from any mail client program or device. Webmail uses IMAP.
IMAP is the preferred protocol for accessing your mail from various locations as well as through multiple devices. For example, having your email address set up on your home computer, a tablet, and a phone, IMAP centralizes the storage of your emails to your DreamHost mail server; as long as you have an Internet connection, you can connect to your IMAP servers to access your mail from anywhere on any device.
Which should I choose?
IMAP is recommended since email is available from any device you choose to connect with. POP downloads the emails to a specific device so it’s possible email could be lost or misplaced.
Use IMAP if you want to check email from multiple computers or devices. Use POP3 if you want your email always accessible, even when there’s no Internet connection. But, be aware that email will only be available on the device to which you downloaded them.
If you have been using IMAP and have some mail stored in folders other than the Inbox, move the emails to the Inbox before using POP3.
Step 2 — Choose a secure or insecure incoming port
Based on your decision to use POP or IMAP, choose the corresponding port number below. Once again, secure IMAP is recommended.
Recommended — Incoming IMAP secure
- IMAP | Port 993 (Secure Transport — SSL function enabled)
Other options
- POP3 | Port 995 (Secure Transport — SSL function enabled)
- IMAP | Port 143 (Insecure Transport — No SSL function enabled)
- POP3 | Port 110 (Insecure Transport — No SSL function enabled)
Step 3 — Choose an outgoing SMTP port
See also: SMTP on Wikipedia, SMTP quota
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is the de facto standard for outgoing email transmissions across the Internet.
Recommended outgoing ports
- SMTP | Port 465 (Secure Transport — SSL function enabled)
- SMTP | Port 587 (Insecure Transport, but can be upgraded to a secure connection using STARTTLS)
Not recommended
- SMTP | Port 25 (Outdated and not recommended. username/password authentication MUST be enabled if using this port.)
Port 465 with SSL is recommended, however some email clients are unable to use this port.
If you are unable to use port 465, the next best option is port 587 using STARTTLS.
Connection security overview
When you choose a secure port number, your connection is secured as an SSL/TLS connection. Below are some of the benefits of using a secure port number.
Encrypted communications
Your login information and email messages are sent in encrypted form, so people can’t eavesdrop on them.
Server authentication
With certificates properly set up, you can check that the IMAP/POP server that you’re connecting to is the correct machine (and not an impostor that just wants to steal your password.) The server provides a certificate (public key) which corresponds to a private key on the IMAP/POP server. Once the client knows that the server’s public key is authentic, it can validate communications from that server.
Secure settings are particularly useful if using public Wi-Fi, which may not be encrypted. Secure settings ensure that people can’t read your email by listening to the network, nor can they (more intrusively) set up a fake email server to capture your emails.
Webmail
You should also use Webmail over a secure (HTTPS) connection. For example:
Some clients will set the port automatically when you select TLS/SSL, or select TLS/SSL automatically when you select the appropriate port. Other clients will require that you make both selections in order to fully configure SSL for the appropriate service.
What is the STARTTLS connection type?
Another method uses STARTTLS. The STARTTLS method connects to the regular SMTP/IMAP/POP3 port and then upgrades the connection to TLS by sending a STARTTLS request. Some email clients refer to this as “TLS” and the method of directly using encryption to a different port as “SSL”. This distinction is technically incorrect!
Examples using a secure IMAP or POP connection
Secure IMAP incoming and outgoing configuration
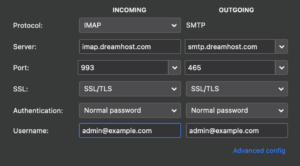
The image above displays a secure IMAP configuration.
This is secure because the ports of 993 (incoming) and 465 (outgoing) are secure port numbers. SSL is also enabled which forces you to use these secure ports.
- The port setting and the SSL option must match each other – i.e., if you’re using SSL/TLS you must use secure ports.
- Enabling SSL (Secure Transport) will require an additional step in confirming and accepting the certificate for the secure connection for both incoming and outgoing mail.
- It’s normal to get a certificate warning when attempting to connect using a secure connection. View the Certificate Domain Mismatch Error article for solutions.
See also
Fonte: Dreamhost.com
